Elastic Load Balancer
EBS Overview
Elastic Load Balancer - ELB Elastic Load Balance is used to automatically distribute incoming traffic across multiple targets such as Amazon EC2 instances, across multiple AZs.
Types of Load Balancers
- Application Load Balancer - Inteligent: are intelligent and best suited for load balancing of HTTP & HTTPS traffic. Application Load balancer operates at layer 7 and is “application-aware”. Makes use of the following to function properly:
- Listeners: To check for connection requests from clients, using the protocol and port you configure.
- Roles: To determine how the load balancer routes the request to its registered target.
- Target Group: Each target group routes requests to its registered targets.
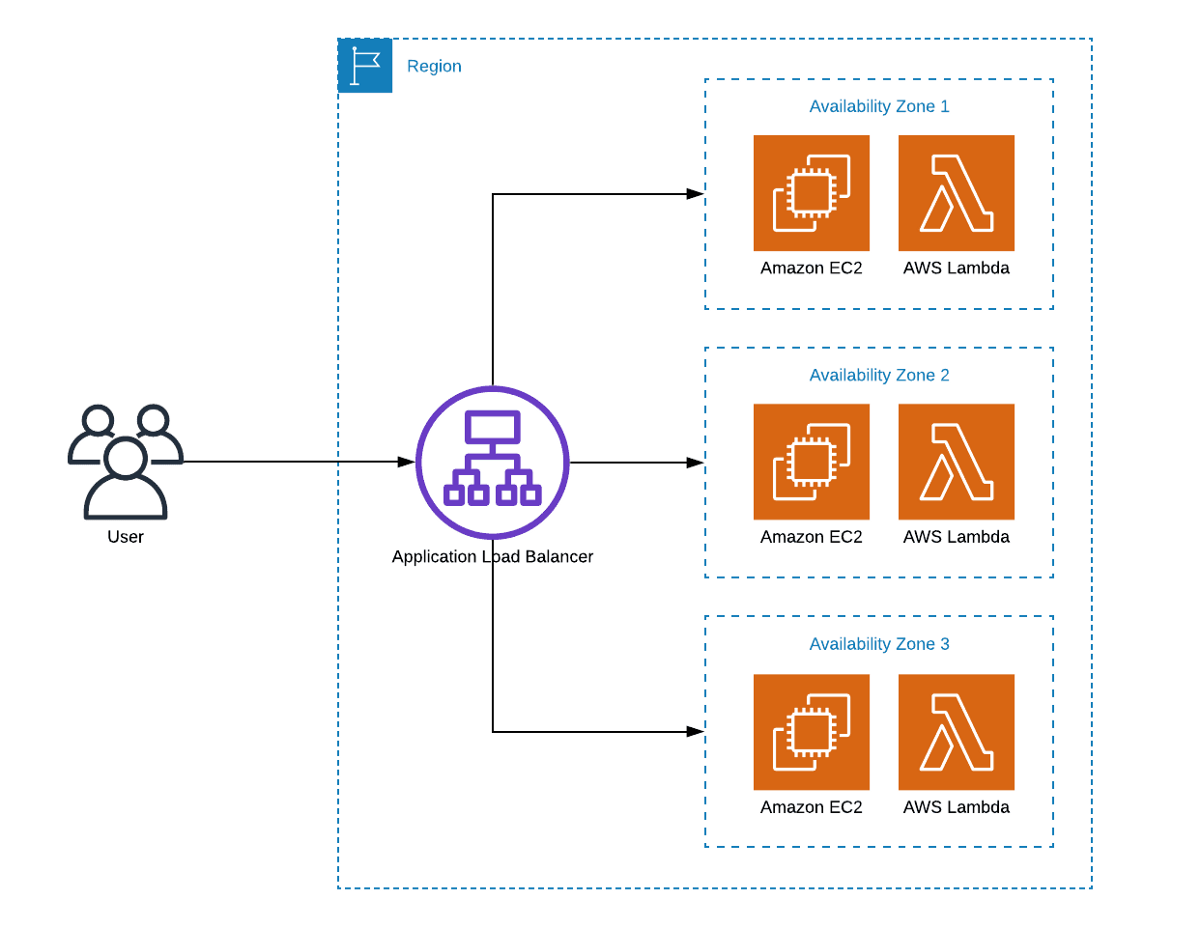
Limitations of Application Load Balancer
- With Application Load Balancer, you can only use HTTP and HTTPS.
- To must deploy at least one SSL/TLS server certificate.
Learns: While provisioning an Application load balancer I got an error 503 temporarily unavailable.. After debugging for some time, I discovered the error was there because I did not register my instances to the target group I created.
- Network Load Balancer - Performance: Operates at layer 4. When performance is a big factor to consider in your solution Network Load Balancer is the best choice because it is capable of handling millions of requests in seconds and maintaining ultra-low latency. It can decrypt traffic but you will need to install SSL certificate, and when needed protocols that are not supported by Application Load Balancer.
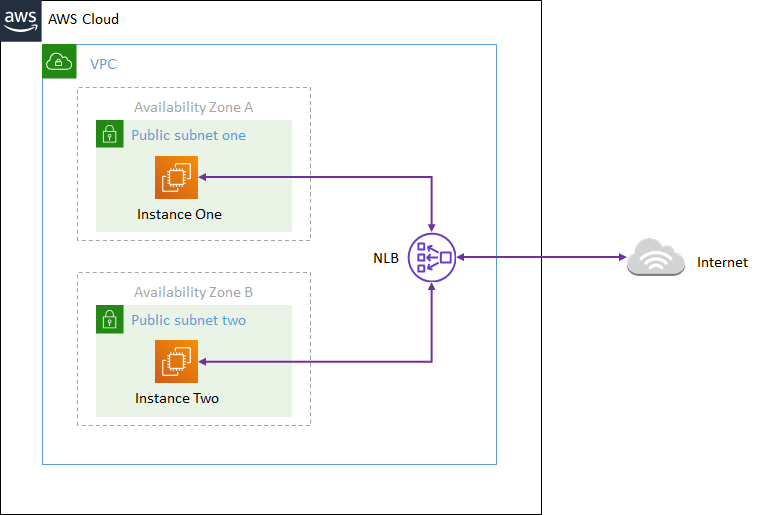
-
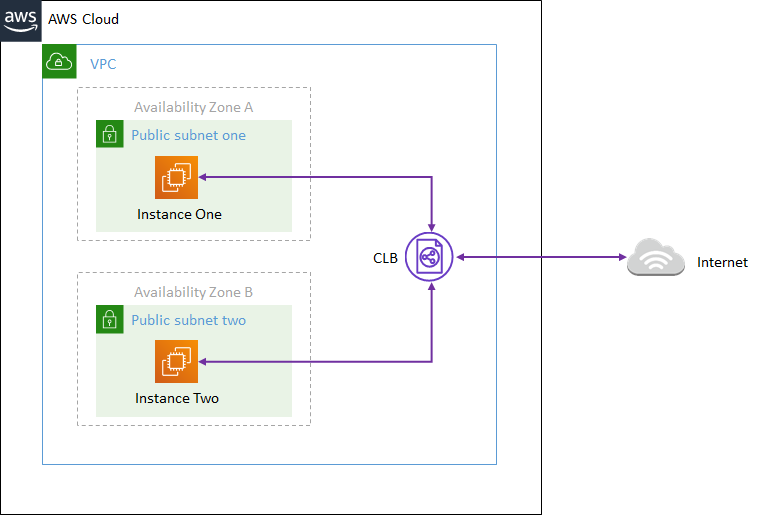
Classic Load Balancer: is a classic legacy load balancer. You can balance HTTP/HTTPS applications and use layer 7-specific features, such as x-forwarded and sticky sessions. You can also use strict layer 4 load balancing for applications that rely on TCP protocol.
-
x-forworded-for: The server access log contains the ip address of the proxy or load balancer only so when traffic is sent from a load balancer, x-forworded-for request header is used to see the ip address of the client. You get error 504 Gateway time out_ if your application has an issue and the classic load balancer cannot reach your application.
-
sticky session: allows you to bind a user session to a specific EC2 instance. Ensures all the requests from the user during the session are sent to the same instance. You can also use a sticky session for Application Load Balancer. But the traffic will be sent at the target group level.
-
Health Checks.
All AWS load balancers can be configured with health checks. Health checks periodically send requests to load balancers’ registered instances to test their status, the status of a healthy load balancer is In Service and the status of an unhealthy load balancer is Out of Service. A health check stops sending requests to a load balancer when the status returns Out of Service.
These notes were taken on A Cloud Guru and the Best practices from AWS Docs